Web Notes
2016.08.20
Using Liquid in Jekyll - Live with Demos
Liquid is a simple template language that Jekyll uses to process pages for your site. With Liquid you can output complex contents without additional plugins.
The URL interface provides properties that allow us to easily read and modify the URL components1.
Use the URL() constructor to create new URL object2:
new URL(url, [base])
url - the full URL or only path (if base is set)base - an optional base URL: if set and url argument has only path, then the URL is generated relative to baseFor example:
let url1 = new URL('https://frankindev.com/hello');
let url2 = new URL('/hello', 'https://frankindev.com');
These two URLs are the same.
We can easily create a new URL based on the path relative to an existing URL:
let url = new URL('https://frankindev.com/hello');
let url_1 = new URL('hello/world', url);
console.log(url_1.href); // https://frankindev.com/hello/world
let url_2 = new URL('./hello', url);
console.log(url_2.href); // https://frankindev.com/hello
let url_3 = new URL('../welcome', url);
console.log(url_3.href); // https://frankindev.com/welcome
For example, https://sb.:pwd@www.frankindev.com:8848/welcome?q=star#top:
URL {
href: 'https://sb.:pwd@www.frankindev.com:8848/welcome?q=star#top',
origin: 'https://www.frankindev.com:8848',
protocol: 'https:',
username: 'sb.',
password: 'pwd',
host: 'www.frankindev.com:8848',
hostname: 'www.frankindev.com',
port: '8848',
pathname: '/welcome',
search: '?q=star',
searchParams: URLSearchParams { 'q' => 'star' },
hash: '#top'
}
href - A string containing the whole URL.origin (read only) - A string containing the origin of the URL, that is its scheme, its domain and its port.protocol - A string containing the protocol scheme of the URL, including the final ':'.username - A string containing the username specified before the domain name.password - A string containing the password specified before the domain name.host - A string containing the domain (i.e., hostname) followed by (if a port was specified) a ':' and the port of the URL.hostname - A string containing the domain of the URL.port - A string containing the port number of the URL.pathname - A string containing an initial '/' followed by the path of the URL, not including the query string or fragment.search - A string indicating the URL’s parameter string; if any parameters are provided, this string includes all of them, beginning with the leading ? character.searchParams (read only) - A URLSearchParams object which can be used to access the individual query parameters found in search.hash - A string containing a '#' followed by the fragment identifier of the URL.Here’s a cheatsheet for URL components:
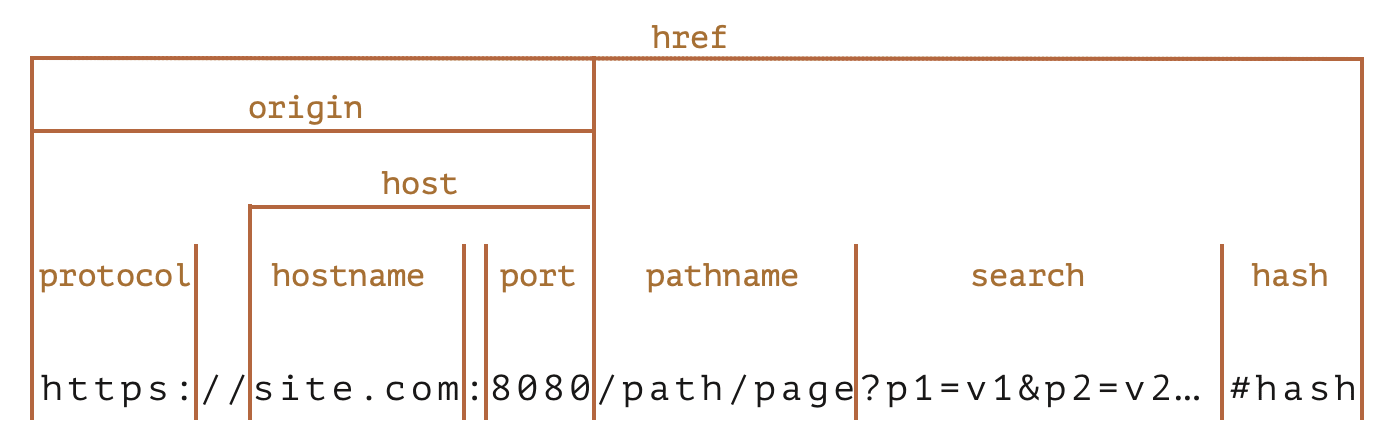
username and password are not parts of the origin.
We can use the
URLobject just like the URL-string where expected, such as infetchorXMLHttpRequest.
Let’s say the URL is https://example.com/?name=Jonathan%20Smith&age=18, we can parse the name and age parameters using:
let params = (new URL(document.location)).searchParams;
let name = params.get('name'); // is the string "Jonathan Smith".
let age = parseInt(params.get('age')); // is the number 18
The parameters used in the URL need to be encoded (according to the rules specified in RFC 3986) if they contain spaces, non-latin letter, etc.
The url.searchParams object also provides convenient methods for search parameters:
append(name, value) - add the parameter by namedelete(name) - remove the parameter by nameget(name) - get the parameter by namegetAll(name) - get all parameters with the same name (e.g., ?user=John&user=Peter)has(name) - check for the existence of the parameter by nameset(name, value) - set/replace the parametersort() - sort parameters by namelet url = new URL('https://google.com/search');
url.searchParams.set('q', 'any words here');
console.log(url.href); // https://google.com/search?q=any+words+here
url.searchParams.set('date', 'year:month:day'); // added parameter with a colon :
// parameters are automatically encoded
console.log(url.href); // https://google.com/search?q=any+words+here&date=year%3Amonth%3Aday
There’re built-in functions for encode/decode special characters:
encodeURI - encodes URL as a wholedecodeURI = decodes it backencodeURIComponent - encodes a URL component, such as search parameter, or a hash, or a pathnamedecodeURIComponent - decodes it backLet’s find the difference between the encodeURI and encodeURIComponent.
For example, in the URL of https://site.com:8080/path/page?p1=v1&p2=v2#hash, characters such as :, ?, =, &, # are allowed. encodeURI will not encode these characters. But for single URL component, characters #, $, &, +, ,, /, :, ;, =, ? and @ are also encoded.
A more specified example:
encodeURI:
let genre = encodeURI('Rock&Roll');
let url = `https://google.com/search?q=${genre}`;
console.log(url); // https://google.com/search?q=Rock&Roll
encodeURIComponent:
let genre = encodeURIComponent('Rock&Roll');
let url = `https://google.com/search?q=${genre}`;
console.log(url); // https://google.com/search?q=Rock%26Roll
As we can see, encodeURI does not encode the & character.
But we should encode & here inside a search parameter, otherwise, we get q=Rock&Roll - that’s actually q=Rock without Roll…
Encoding difference compared to
URLClasses URL and URLSearchParams are based on the latest URI specification: RFC3986, while
encodeURIandencodeURIComponentfunctions are based on the obsolete version RFC2396.There are a few differences, e.g. IPv6 addresses are encoded differently:
// valid url with IPv6 address let url = 'http://[2607:f8b0:4005:802::1007]/'; alert(encodeURI(url)); // http://%5B2607:f8b0:4005:802::1007%5D/ alert(new URL(url)); // http://[2607:f8b0:4005:802::1007]/As we can see,
encodeURIreplaced square brackets[...], that’s not correct, the reason is: IPv6 urls did not exist at the time of RFC2396 (August 1998).
Frank Lin
Web Notes
2016.08.20
Liquid is a simple template language that Jekyll uses to process pages for your site. With Liquid you can output complex contents without additional plugins.
Tutorials
2020.01.09
IKEv2, or Internet Key Exchange v2, is a protocol that allows for direct IPSec tunnelling between networks. It is developed by Microsoft and Cisco (primarily) for mobile users, and introduced as an updated version of IKEv1 in 2005. The IKEv2 MOBIKE (Mobility and Multihoming) protocol allows the client to main secure connection despite network switches, such as when leaving a WiFi area for a mobile data area. IKEv2 works on most platforms, and natively supported on some platforms (OS X 10.11+, iOS 9.1+, and Windows 10) with no additional applications necessary.
JavaScript Notes
2018.12.17
JavaScript is a very function-oriented language. As we know, functions are first class objects and can be easily assigned to variables, passed as arguments, returned from another function invocation, or stored into data structures. A function can access variable outside of it. But what happens when an outer variable changes? Does a function get the most recent value or the one that existed when the function was created? Also, what happens when a function invoked in another place - does it get access to the outer variables of the new place?