In JavaScript, a callback is a function that is passed as an argument to another function and is invoked with the result when the operation completes. In functional programming, this way of propagating the result is called continuation-passing style (CPS). It simply indicates that a result is propagated by passing it to another function (the callback), instead of directly returning it to the caller.
Synchronous Continuation-Passing Style
Let’s take a look at a simple synchronous function:
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
This is the so-called direct style that represents the most common way of returning a result in synchronous programming. The result is directly passed back to the caller using the return instruction. An equivalent continuation-passing style of the preceding function would be:
function add(a, b, callback) {
callback(a + b);
}
Now the add() function is a synchronous CPS function, which means that it will return a value only when the callback function completes its execution.
Asynchronous Continuation-Passing Style
Let’s make the preceding function asynchronous:
function addAsync(a, b, callback) {
setTimeout(function() {
callback(a + b);
}, 100);
}
The setTimeout() is used to simulate an asynchronous invocation of the callback.
Now, let’s try to use this function and see how the order of the operations:
console.log('before');
addAsync(1, 2, function(result) {
console.log('Result: ' + result);
});
console.log('after');
// before
// after
// Result: 3
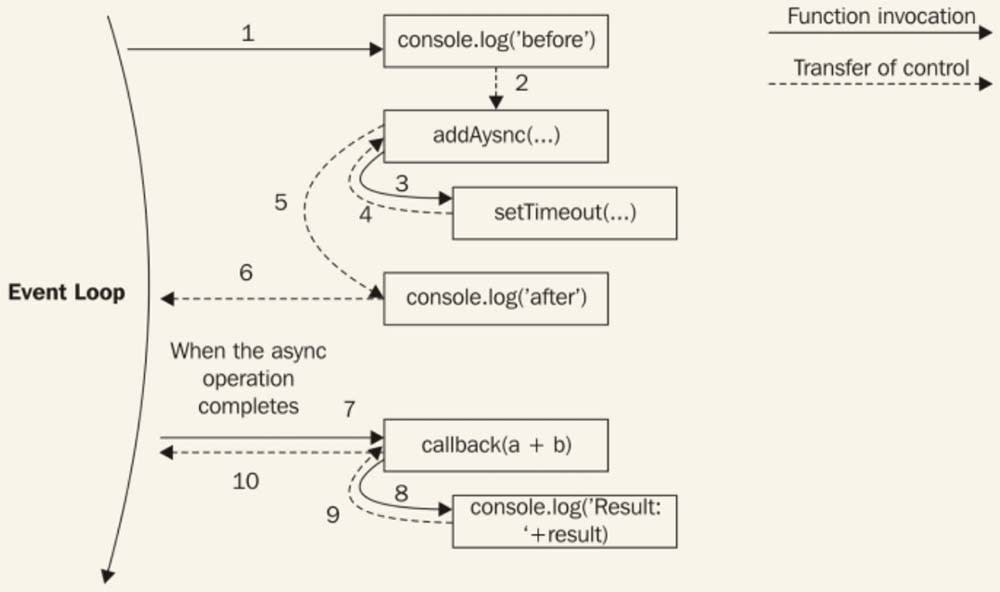
Since setTimeout() triggers an asynchronous operation, it will not wait anymore for the callback to be executed, but instead, it returns immediately giving the control back to addAsync(), and then back to its caller. The following image shows how this works:

When the asynchronous operation completes, the execution is then resumed starting from the callback provided to the asynchronous function that caused the unwinding. The execution will start from the Event Loop, so it will have a fresh stack. Thanks to closures in JavaScript, it is trivial to maintain the context of the caller of the asynchronous function, even if the callback is invoked at a different point in time and from a different location.
Non Continuation-Passing Style Callbacks
There’re several circumstances in which the presence of a callback argument might make you think that a function is asynchronous or is using a continuation-passing style; that’s not always true, let’s take, for instance, the map() method of the Array object:
let result = [1, 2, 7].map(function(element) {
return element + 1;
})
The callback is just used to iterate over the elements of the array, and not to pass the result of the operation. The result is returned synchronously using a direct style.